Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (41): 6614-6619.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.41.010
Previous Articles Next Articles
Biological characteristics of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells: cold trypsin digestion versus tissue explant method in vitro
Zhang Fei, Wang Yi-xiong, Wu Zhong-yan, Li Gui-cai, Cao Peng, Wang Wu
- Department of Orthopedic Surgery, the Fifth Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830001, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China
-
Revised:2014-09-20Online:2014-10-01Published:2014-10-01 -
Contact:Wu Zhong-yan, Chief physician, Professor, Master’s supervisor, Department of Orthopedic Surgery, the Fifth Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830001, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Zhang Fei, Studying for master’s degree, Department of Orthopedic Surgery, the Fifth Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830001, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:Medical Research and Innovation Fund of Xinjiang Medical University, No. XJC2012117
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhang Fei, Wang Yi-xiong, Wu Zhong-yan, Li Gui-cai, Cao Peng, Wang Wu. Biological characteristics of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells: cold trypsin digestion versus tissue explant method in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(41): 6614-6619.
share this article
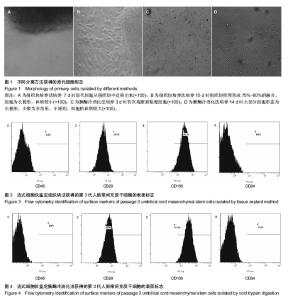
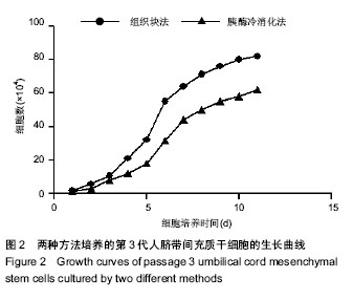
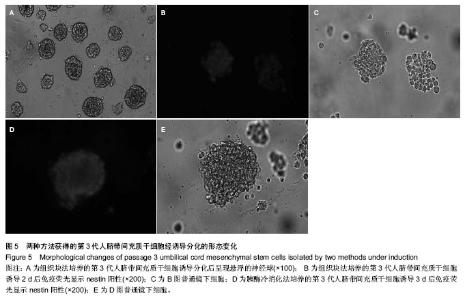
2.1 两种方法培养的原代脐带间充质干细胞最早出现时间及培养周期 使用上述两种方法均可获得人脐带间充质干细胞,组织块法在种植后第5-7天才见到细胞从组织块爬出,最早观察细胞贴壁时间为(5.80±0.84) d,而胰酶冷消化法在消化种植后第2,3天就可见到细胞贴壁生长,最早观察细胞贴壁时间为(2.60±0.55) d,差异有显著性意义 (P < 0.05)。但两种方法得到的原代细胞达到90%-95%融合的时间差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),组织块法为(14.4± 1.67) d,胰酶冷消化法为(14.6±0.90) d。 2.2 两种方法培养的脐带间充质干细胞形态观察及生长情况 胰酶冷消化法培养两三天就可见单个贴壁细胞,呈圆形或短梭形,培养10 d左右,细胞形态逐渐伸展开来,大体呈长梭形,但少数细胞边缘不光滑,为多角形,不规则,细胞的体积较大,培养2周之后,细胞已逐渐形成漩涡状的集落,且逐渐变大,细胞增多,即可传代。传代后的细胞生长速度明显增快,数量增多,四五天即可传代1次。组织块法培养5 d左右亦可观察到个别细胞沿组织块边缘爬出,呈短梭形、纤细;随后细胞数量增多,慢慢向外扩长,形态类似成纤维细胞,并逐渐形成漩涡状的集落,培养13-16 d,可见细胞集落逐渐变大,细胞增多,即可传代,见图1。 2.3 第3代人脐带间充质干细胞的生长曲线 两组细胞的增殖曲线近似“S”型,细胞种植后第一二天处于潜伏期,从第3天起细胞开始进入对数增殖期,于第8天左右进入平台期;组织块法获得第3代细胞的增殖速率显著快于胰酶冷消化法,在进入对数生长期后的各个时间点细胞数量差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),见图2。 2.4 两种方法培养的脐带间充质干细胞表面抗原检测 为了明确脐带来源贴壁生长细胞是否与骨髓间充质干细胞具有相同的抗原标志表达,取上述第3代脐带间充质干细胞样细胞经流式细胞仪检测,结果显示,上述细胞不表达CD34,CD45,而表达CD29、CD105(图3,4),即表达了骨髓间充质干细胞的常见抗原标志。 2.5 两种方法培养的脐带间充质干细胞向神经干细胞多向分化的潜能 两种方法培养出来的第3代人脐带间充质干细胞加入诱导液后第2天均可看到部分细胞聚集成团漂浮于诱导液当中,呈椭圆形或圆形,随着诱导时间增长,漂浮的神经球样细胞越来越多,且越来越大,免疫荧光显示神经球样细胞表达神经干细胞特征性标志物nestin阳性,见图5。"
| [1] 马锡慧,冯凯,石炳毅.人脐带间充质干细胞生物学特性及其研究进展[J].中国组织工程研究,2011,15(32):6064-6067.
[2] Zhang YN, Lie PC, Wei X.Differentiation of mesenchymal stromal cells derived from umbilical cord Wharton's jelly into hepatocyte-like cells.Cytotherapy. 2009;11(5):548-558.
[3] Woodbury D, Schwarz EJ, Prockop DJ, et al.Adult rat and human bone marrow stromal cells differentiate into neurons.J Neurosci Res. 2000;61(4):364-370.
[4] Paldino E, Cenciarelli C, Giampaolo A,et al.Induction of dopaminergic neurons from human Wharton's jelly mesenchymal stem cell by forskolin.J Cell Physiol. 2014; 229(2):232-244.
[5] Alves da Silva ML, Costa-Pinto AR, Martins A,et al. Conditioned medium as a strategy for human stem cells chondrogenic differentiation.J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2013 Oct 24. doi: 10.1002/term.1812. [Epub ahead of print].
[6] McElreavey KD, Irvine AI, Ennis KT,et al.Isolation, culture and characterisation of fibroblast-like cells derived from the Wharton's jelly portion of human umbilical cord.Biochem Soc Trans. 1991;19(1):29S.
[7] Mueller SM, Glowacki J.Age-related decline in the osteogenic potential of human bone marrow cells cultured in three- imensional collagen sponges.J Cell Biochem. 2001;82(4): 583-590.
[8] 庞荣清,何洁,李福兵,等.一种简单的人脐带间充质干细胞分离培养方法[J/CD]/中华细胞与干细胞杂志:电子版,2011,1(2):30-33.
[9] 唐欣,王岩,易海波,等.人脐带间充质干细胞诱导分化为心肌细胞的特异性基因表达[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(27):4988- 4991.
[10] 王跃春,李业霞,段阿林,等.人脐带间充质干细胞的快速分离、纯化及冻存[J].中国病理生理杂志,2010,26(8):1658-1661.
[11] Shaer A, Azarpira N, Aghdaie MH,et al.Isolation and characterization of Human Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Derived from Placental Decidua Basalis; Umbilical cord Wharton's Jelly and Amniotic Membrane.Pak J Med Sci. 2014; 30(5):1022-1026.
[12] Tsai PJ, Wang HS, Lin GJ,et al.Undifferentiated Wharton?s Jelly Mesenchymal Stem Cell Transplantation Induces Insulin-Producing Cell Differentiation and Suppression of T Cell-Mediated Autoimmunity in Non-Obese Diabetic Mice.Cell Transplant. 2014 Jul 15. [Epub ahead of print]
[13] Constantinescu A, Andrei E, Iordache F,et al.Recellularization potential assessment of Wharton's Jelly-derived endothelial progenitor cells using a human fetal vascular tissue model.In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2014 Aug 15. [Epub ahead of print]
[14] Ribeiro J, Pereira T, Amorim I,et al.Cell therapy with human MSCs isolated from the umbilical cord Wharton jelly associated to a PVA membrane in the treatment of chronic skin wounds.Int J Med Sci. 2014;11(10):979-987.
[15] Alunno A, Montanucci P, Bistoni O,et al. In vitro immunomodulatory effects of microencapsulated umbilical cord Wharton jelly-derived mesenchymal stem cells in primary Sjögren's syndrome.Rheumatology (Oxford). 2014 Jul 26. pii: keu292. [Epub ahead of print].
[16] 马海英,李丽,马玲,等.组织块贴壁法提取胎盘、脐带和胎膜间充质干细胞效果观察[J].山东医药,2011,51(15):39-41.
[17] 蒋知新,艾民,张清华,等.体外原代培养脐带基质间充质细胞和人皮肤成纤维细胞[J].中国老年学杂志,2012,32(19):4193-4194.
[18] 刘玲英,柴家科,段红杰,等.人脐带间充质干细胞不同分离方法的效果比较[J].中华医学杂志,2013,93(32):2592-2596.
[19] 侯克东,许文静,张莉,等.人脐带Wharton胶中间充质干细胞向软骨诱导的实验研究[J].中华骨科杂志,2007,27(12):930-935.
[20] 郝白露,杨瑞峰,彭祥炽,等.改良的人脐带间充质干细胞培养方法[J].中国计划生育学杂志,2013,21(1):44-49.
[21] 庞荣清,何洁,李福兵,等.一种简单的人脐带间充质干细胞分离培养方法[J].中华细胞与干细胞杂志:电子版,2011,1(2):30-33.
[22] 王绮雯,吴启端,陈奕芝.温胰蛋白酶消化法和冷消化法培养乳鼠心肌细胞的比较[J].中国医药指南,2013,11(20):401-403.
[23] 刘巨超,周海洋,孙慧伟,等.工程化肝组织肝表面片状植入新方法[J].中华实验外科杂志,2012,29(5):880-882.
[24] Massood E, Maryam K, Parvin S,et al.Vitrification of human umbilical cord Wharton's jelly-derived mesenchymal stem cells.Cryo Letters. 2013;34(5):471-480.
[25] Tantrawatpan C, Manochantr S, Kheolamai P,et al.Pluripotent gene expression in mesenchymal stem cells from human umbilical cord Wharton's jelly and their differentiation potential to neural-like cells.J Med Assoc Thai. 2013;96(9):1208-1217.
[26] Mikaeili Agah E, Parivar K, Nabiuni M,et al.Induction of human umbilical Wharton's jelly-derived stem cells toward oligodendrocyte phenotype.J Mol Neurosci. 2013;51(2): 328-336.
[27] Messerli M, Wagner A, Sager R,et al.Stem cells from umbilical cord Wharton's jelly from preterm birth have neuroglial differentiation potential.Reprod Sci. 2013;20(12):1455-1464.
[28] Kim MJ, Shin KS, Jeon JH,et al.Human chorionic-plate-derived mesenchymal stem cells and Wharton's jelly-derived mesenchymal stem cells: a comparative analysis of their potential as placenta-derived stem cells.Cell Tissue Res. 2011;346(1):53-64.
[29] Baksh D, Yao R, Tuan RS.Comparison of proliferative and multilineage differentiation potential of human mesenchymal stem cells derived from umbilical cord and bone marrow.Stem Cells. 2007;25(6):1384-1392.
[30] De Bruyn C, Najar M, Raicevic G,et al.A rapid, simple, and reproducible method for the isolation of mesenchymal stromal cells from Wharton's jelly without enzymatic treatment.Stem Cells Dev. 2011;20(3):547-557.
[31] Weiss ML, Anderson C, Medicetty S, et al.Immune properties of human umbilical cord Wharton's jelly-derived cells.Stem Cells. 2008;26(11):2865-2874.
[32] Karahuseyinoglu S, Cinar O, Kilic E,et al.Biology of stem cells in human umbilical cord stroma: in situ and in vitro surveys. Stem Cells. 2007;25(2):319-331.
[33] Hu Y, Liang J, Cui H,et al.Wharton's jelly mesenchymal stem cells differentiate into retinal progenitor cells.Neural Regen Res. 2013;8(19):1783-1792.
[34] Joerger-Messerli M, Brühlmann E, Bessire A,et al. Preeclampsia enhances neuroglial marker expression in umbilical cord Wharton's jelly-derived mesenchymal stem cells.J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2014:1-6.
[35] Yan M, Sun M, Zhou Y,et al.Conversion of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells in Wharton's jelly to dopamine neurons mediated by the Lmx1a and neurturin in vitro: potential therapeutic application for Parkinson's disease in a rhesus monkey model.PLoS One. 2013;8(5):e64000.
[36] Balasubramanian S, Thej C, Venugopal P,et al.Higher propensity of Wharton's jelly derived mesenchymal stromal cells towards neuronal lineage in comparison to those derived from adipose and bone marrow.Cell Biol Int. 2013;37(5): 507-515.
[37] 周剑云,孙炜,张新,等.人脐带源神经干细胞的培养和分化[J].中国康复理论与实践,2012, 18(7): 615-618.
[38] 李伟伟,姚星宇,杨丽敏,等.体外诱导人脐带间充质干细胞向神经干细胞的分化[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(1):75-80. |
| [1] | Wang Jian-ji, Yang Long, Li Jing, Sun Qi, Zuo Wei-min, Ren Qi-feng, Sun Yu, Wu Zhan-yu, Zou Qiang, Ma Min-xian, Ye Chuan. Development and application of special-purpose grafter by femoral head decompression combined with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells transplantation based on three-dimensional printing technology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(44): 6636-6642. |
| [2] | Li Su-juan, Yuan Wen-chang, Mai Yun-pei, Hou Ning. Adenoviral vectors carrying Brahma-related gene 1 attenuates oxidative stress-induced apoptosis of cardiomyocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(40): 6021-6027. |
| [3] | Zhou Chang-yan, Zhou Qing-huan, Bian Jing, Chen Ke, Chen Wen. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells combined with calcium phosphate cement to repair articular cartilage defects in rabbits [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(8): 1195-1199. |
| [4] | Xu Xiang, Yin He-ping. Platelet-rich plasma accelerates the proliferation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(14): 2144-2148. |
| [5] | Ruan Guang-ping, Yao Xiang, Liu Ju-fen, Wang Jin-xiang, Hu Yuan-yuan, Li Zi-an, Yang Jian-yong, Pang Rong-qing, Pan Xing-hua. Transplantation of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(14): 2172-2178. |
| [6] | Jiang Yan-jie, Mao Cheng-gang, Ning Xian-feng, Li Rong, Li Zi-pu. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells via intramuscular injection influence the expression of cytokines related to dilated cardiomyopathy in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(14): 2179-2185. |
| [7] |
Liu Yu-liang, Li Jun, He Yu-qin, Zhuo Feng, Wei Kai-bin.
Transplantation of human umbilical cord derived-mesenchymal stem cells by different ways for the treatment of spinal cord injury
|
| [8] | Gao Zhuo-yue, Liu Yong-qi, He Jian-xin, Wu Zhi-wei, Luo Ya-li, Su Yun, Zhang Li-ying, Zhang Qi, Wu You-ming, Zhou Ni-na. Regulatory effects of warming yang and invigorating qi treatment on the inflammatory balance and genetic stability of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells under tumor microenvironment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(14): 2267-2272. |
| [9] | Liang Liang, Xu Tao, Song Yang, Sheng Wei-bin. siRNA lentiviral vectors carrying telomerase reverse transcriptase gene hasten astrocytes apoptosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(11): 1707-1711. |
| [10] | Han Xiang-zhen, He Hui-yu, Hu Yang, Ba Jiao-jiao, Wang Huan-huan, Mi Xue, Abulizi•Abudula. Recombinant lentiviral vector transfected sheep bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and osteogenic gene expression changes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(6): 821-828. |
| [11] | Huang Jian-feng, Huang Ji-feng, Zhang Wei-cai. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells differentiate into neuron-like cells induced by combination of two cytokines [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(6): 829-834. |
| [12] | Zou Bin, Zong Shao-hui, Zeng Gao-feng, Fang Ye, Gao Tai-hang. Effects of alpha-zearalanol on the osteogenic differentiation of mouse bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(6): 835-840. |
| [13] | Yang Yi, Ding Wen-jing, Dong Wan-li. Autophagy-related gene Beclin-1 expression in neuron-like differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(6): 841-846. |
| [14] | Su Xue-lian, Bao Guang-jie, Kang Hong, Liu Lin, Kong Nan-nan. Morphological changes of goat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells differentiating into fibrochondrocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(6): 860-865. |
| [15] | Wang Chan, Dai Ying, Guo Yong-long, Yang Yan, Liu Qing, Chen Jian-su. Three-dimensional spherical culture of adipose-derived stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(6): 872-879. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||